Hiking Map App development is booming. The outdoor recreation market is exploding, and with it, the demand for robust, user-friendly apps to guide adventurers through trails, mountains, and wilderness areas. This guide dives deep into the creation and monetization of a successful hiking map app, covering everything from market analysis and feature design to UX/UI considerations and technical implementation.
We’ll explore the competitive landscape, dissect successful strategies, and provide actionable insights to help you build a top-performing app.
From understanding the critical need for offline functionality and accurate GPS tracking to designing an intuitive user interface and implementing effective monetization strategies, we’ll cover every aspect of building a compelling hiking app. We’ll also examine the challenges of maintaining accurate map data, ensuring data security, and choosing the right technologies for location-based services. This comprehensive guide provides a roadmap for navigating the complexities of app development and achieving success in this growing market.
Features and Functionality: Hiking Map App
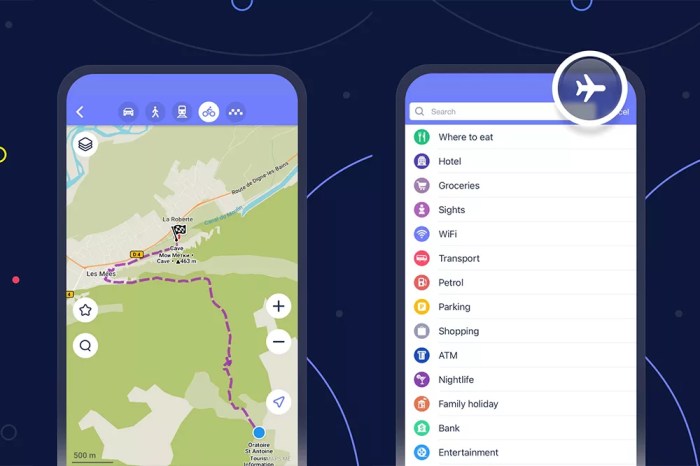
Building a successful hiking app hinges on providing a seamless and reliable user experience. This means offering features that go beyond simply displaying a map; it means anticipating the needs of hikers at every level, from novice to expert. The key is to deliver a powerful, yet intuitive, tool that enhances the hiking experience, not detracts from it.
Offline Map Functionality, Hiking Map App
Offline map functionality is absolutely crucial for any serious hiking app. Imagine being miles from civilization, relying on your phone for navigation, only to discover you’ve lost cell service. This isn’t a hypothetical scenario; it’s a reality for many hikers. By allowing users to download map tiles for offline use, you eliminate this critical point of failure.
This feature provides peace of mind, allowing hikers to explore remote areas with confidence, knowing they won’t be left stranded due to a lack of network connectivity. The ability to pre-download maps significantly increases the app’s usability and reliability, particularly in areas with poor or nonexistent cell service, making it a must-have feature for any competitive hiking app.
GPS Tracking Integration: Benefits and Drawbacks
Integrating GPS tracking offers significant benefits, such as real-time location tracking, the ability to record routes for later review and sharing, and the calculation of distance traveled and elevation gain. Hikers can use this data to monitor their progress, plan future hikes, and share their adventures with others. However, continuous GPS tracking drains battery life considerably. This is a significant drawback, especially on longer hikes.
To mitigate this, consider offering options for different tracking frequencies (e.g., high accuracy, battery saving) and providing clear warnings about battery consumption. Furthermore, concerns around data privacy need to be addressed transparently, providing users with clear control over their data and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
Augmented Reality Trail Overlays
Imagine this: you’re on a trail, your phone displays a live view of your surroundings through the camera, and a translucent overlay shows you the trail ahead, highlighting key points of interest, upcoming turns, and potential hazards. This is the power of augmented reality (AR) trail overlays. The user interface should be clean and uncluttered. The AR overlay should be easily toggled on and off, and the transparency level adjustable to suit different lighting conditions.
Key information, such as distance to the next waypoint, should be displayed prominently but unobtrusively. The AR view should seamlessly integrate with the traditional map view, allowing users to switch between them effortlessly. Think of it as a heads-up display for hikers, providing real-time guidance without requiring constant map consultation.
Essential Map Features by Hiking Difficulty Level
Providing the right features for each hiking level is crucial. A beginner hiker doesn’t need the same level of detail as an experienced mountaineer.
- Beginner: Simple trail map, elevation profile, distance markers, points of interest (e.g., restrooms, water sources), clear route indication, emergency contact information.
- Intermediate: All beginner features plus detailed topographic maps, compass functionality, ability to create custom routes, offline map support, trail difficulty ratings, user-submitted reviews and photos.
- Expert: All intermediate features plus advanced topographic maps, support for various map projections, GPS track recording with detailed analysis, integration with weather forecasts, route planning tools for complex terrain, integration with external sensors (e.g., heart rate monitor).
User Experience (UX) and Design
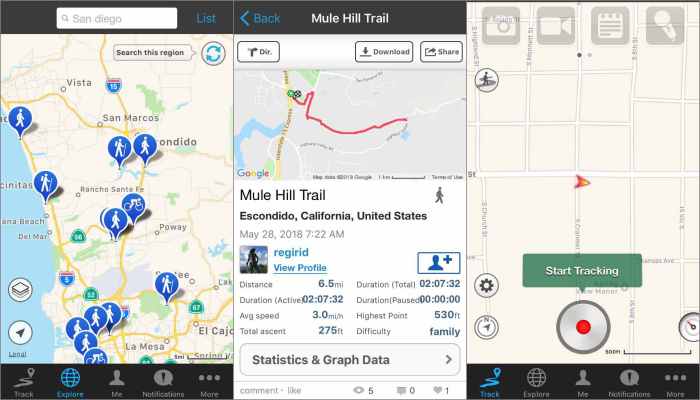
Creating a top-tier hiking map app isn’t just about displaying trails; it’s about crafting an experience that seamlessly blends technology with the thrill of the outdoors. The user interface must be intuitive, visually appealing, and robust enough to handle various scenarios, from planning a leisurely stroll to navigating challenging backcountry routes. A poorly designed app can quickly turn a potential adventure into a frustrating ordeal, driving users away and impacting your app’s success.The design considerations for a hiking map app must prioritize clarity, efficiency, and ease of use.
Every element, from the map itself to the trail information displayed, should be strategically placed and designed to minimize cognitive load and maximize user satisfaction. Think of it like this: the app should be so intuitive that even a novice hiker can effortlessly plan and execute a hike.
Map Interface Design Considerations
The core of any hiking map app is its map interface. It needs to be highly responsive, displaying a clear and detailed map with readily accessible trail information. Key design elements include high-resolution topographic maps with clear trail markings, customizable map overlays (satellite imagery, terrain shading), intuitive zoom and pan controls, and a prominent location marker showing the user’s current position.
Consider incorporating features like offline map caching for areas with limited or no cellular service—a crucial aspect for ensuring safety and reliability in remote locations. Furthermore, the color scheme should be carefully chosen to ensure readability and visual appeal, even under bright sunlight. Think vibrant, easily distinguishable colors for trails and points of interest, contrasting sharply against the map background.
AllTrails, for example, excels in this area with its clear trail markings and user-friendly interface.
Usability Testing Methods
Thorough usability testing is critical for identifying and addressing potential pain points before the app’s launch. Several methods can be employed to ensure a positive user experience.
A range of methods should be used to get a complete picture of user experience. These include:
- A/B Testing: Compare different design iterations to determine which performs better.
- Focus Groups: Gather feedback from target users through guided discussions.
- Heuristic Evaluation: Have usability experts assess the app against established usability principles.
- User Interviews: Conduct one-on-one interviews to gain in-depth insights into user behavior and preferences.
- Think-Aloud Protocol: Have users verbalize their thoughts while using the app to understand their decision-making process.
Improving Trail Discoverability
Effective trail discovery is crucial for a hiking map app’s success. This involves leveraging user location data and preferences to intelligently suggest relevant trails.
The key to effective trail discovery is personalization and relevance. Here’s how:
- Location-Based Suggestions: Prioritize trails near the user’s current location or a specified destination. For instance, if a user is in Yosemite National Park, the app should prominently feature trails within the park.
- Preference-Based Filtering: Allow users to filter trails based on criteria like difficulty level, distance, elevation gain, and type of terrain (e.g., forest, mountain, desert). This allows users to quickly find trails that match their fitness level and preferences.
- Recommendation Engine: Implement a recommendation engine that suggests trails based on the user’s past activity and preferences. This could be similar to Netflix’s recommendation system, suggesting trails based on trails the user has previously hiked or expressed interest in.
- Search Functionality: Provide a robust search function that allows users to search for trails by name, location, or s (e.g., “waterfalls,” “scenic views”).
Ideal User Flow for Planning and Completing a Hike
The ideal user flow should be smooth and intuitive, guiding users through the entire process from planning to completing their hike.
A streamlined user flow is crucial for user engagement. Here’s how it should work:
- Search/Discovery: The user initiates a search based on location, preferences, or s.
- Trail Selection: The user reviews trail details (map, elevation profile, difficulty, reviews) and selects a trail.
- Navigation: The app provides turn-by-turn navigation, utilizing GPS to guide the user along the selected trail.
- Offline Maps: The app allows for downloading maps for offline use in areas with poor or no cell service.
- Safety Features: The app incorporates safety features like emergency contact information, SOS buttons, and live location sharing.
- Post-Hike Review: The user can review and rate the trail after completion, providing valuable feedback for other users.
Creating a successful Hiking Map App requires a blend of strategic planning, innovative design, and robust technical execution. By carefully analyzing the market, understanding user needs, and implementing effective monetization strategies, you can build an app that not only meets user demands but also generates substantial revenue. Remember, a user-centric approach, coupled with a commitment to accuracy and data security, is crucial for building a thriving and sustainable hiking map application.
Don’t just build an app; build an experience that helps people explore and connect with the outdoors.

